Previously, cervical cancer survival rates were so poor amongst women. In fact, a long time ago, this type of cancer was the most common cause of cancer death in women. However, in the last 30 years, the mortality rate has decreased by 50% because of the widespread utilization of Pap smear.
In 2004, there were approximately 10,500 new cases of invasive cervical cancer and more than 50,000 cases of carcinoma in situ. There were 3,900 cases of reported death from this disease, but about 85% of them were due to the lack of preventative and detective methods like Pap smear.
Pap smear has an accuracy of almost 90 to 95% in diagnosing early lesions such as CIN. The only disadvantage is that it lacks the diagnostic sensitivity to detect cancer when the tumor or mass is thoroughly invaded with fungus. Inflammation, necrosis and hemorrhage can give false positive smears, and a proper biopsy may have to be used to confirm the existence of cancer. The American Cancer Society recommends that women who live an active sex life or those who are already at the age of 20 undergo annual smears for two consecutive years. If they are negative, the smear should be repeated every three years. This is seconded by American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology as well.
Cervical Cancer Survival Rates by Stage
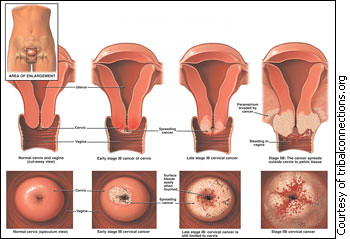
Stage 0 is also what they call carcinoma in situ while stage I has a tumor that is confined to the cervix. Stage II indicates that the invasion has gone beyond the cervix but does not reach the wall of the pelvis and the lower third of the vagina. Stage III has a tumor that invades the wall of the pelvis or lower third of the vagina or causes hydronephrosis while lastly, stage IV is manifested by invasion of the mucosa of the bladder or rectum or an extension beyond the true pelvis.
Cervical Cancer Survival Rates at five years are reported as follows: stage I: 85%; stage II: 60%; stage III: 33%; and stage IV: 7%.
Carcinoma in situ (stage 0) can be treated successfully by excision of a cone of tissue or abdominal hysterectomy. In stage I the results are apparently comparable with radical hysterectomy and radiotherapy. Patients in stages II to IV are treated primarily with radical radiotherapy or combined modality treatment. Retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy has no proven therapeutic value. Pelvic evisceration, although rare, is performed to treat cancers that cause persistent or recurrent central. After this, intervention is often possible to reconstruct the vagina, bladder and rectum.
In women with locally advanced stages (stages IIB to IVA), cervical cancer survival rates are improved by administering platinum-based chemotherapy along with radiation therapy compared to treatment with radiation alone.